- MATLAB — Интеграция
- Поиск неопределенного интеграла с помощью MATLAB
- Пример 1
- Пример 2
- Вычислить площадь под графиком матлаб
- Syntax
- Description
- Examples
- Create Area Plot with One Curve
- Create Area Plot with Multiple Curves
- Create Area Plot Using Horizontal Axis Values
- Adjust Baseline Value of Area Plot
- Specify Line Style of Area Plot
- Plot Filled Area into Target Axes
- Change Area Characteristics After Plotting
- Set Colors in Area Plot
- Input Arguments
- X — x-coordinates vector | matrix
- Y — y-coordinates vector | matrix
- basevalue — Baseline value 0 (default) | numeric scalar
- ax — Target axes Axes object
- Name-Value Arguments
- FaceColor — Area fill color RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | ‘r’ | ‘g’ | ‘b’ | ‘flat’ | .
- Matlab, как рассчитать AUC (площадь под кривой)?
- 6 ответов
- 🎥 Видео
Видео:Построение графиков: нахождение площади под кривойСкачать
MATLAB — Интеграция
Интеграция имеет дело с двумя принципиально разными типами проблем.
В первом типе дается производная функции, и мы хотим найти функцию. Поэтому мы в основном обращаем вспять процесс дифференциации. Этот обратный процесс известен как антидифференцирование, или нахождение примитивной функции, или нахождение неопределенного интеграла .
Второй тип проблем включает сложение очень большого количества очень маленьких величин, а затем определение предела, когда размер величин приближается к нулю, а число членов стремится к бесконечности. Этот процесс приводит к определению определенного интеграла .
В первом типе дается производная функции, и мы хотим найти функцию. Поэтому мы в основном обращаем вспять процесс дифференциации. Этот обратный процесс известен как антидифференцирование, или нахождение примитивной функции, или нахождение неопределенного интеграла .
Второй тип проблем включает сложение очень большого количества очень маленьких величин, а затем определение предела, когда размер величин приближается к нулю, а число членов стремится к бесконечности. Этот процесс приводит к определению определенного интеграла .
Определенные интегралы используются для определения площади, объема, центра тяжести, момента инерции, работы, выполняемой силой, и во многих других приложениях.
Видео:MATLAB 07 Интерактивное построение графиковСкачать

Поиск неопределенного интеграла с помощью MATLAB
По определению, если производная функции f (x) есть f ‘(x), то мы говорим, что неопределенный интеграл от f’ (x) по x равен f (x). Например, поскольку производная (по x) x 2 равна 2x, мы можем сказать, что неопределенный интеграл от 2x равен x 2 .
f ‘(x 2 ) = 2x , следовательно,
Неопределенный интеграл не является уникальным, потому что производная x 2 + c для любого значения константы c также будет 2x.
Это выражается в символах как —
Где c называется «произвольной константой».
MATLAB предоставляет команду int для вычисления интеграла выражения. Чтобы вывести выражение для неопределенного интеграла функции, мы пишем —
Например, из нашего предыдущего примера —
MATLAB выполняет приведенный выше оператор и возвращает следующий результат —
Пример 1
В этом примере давайте найдем интеграл некоторых часто используемых выражений. Создайте файл сценария и введите в нем следующий код —
Когда вы запускаете файл, он показывает следующий результат —
Пример 2
Создайте файл сценария и введите в нем следующий код —
Обратите внимание, что функция pretty возвращает выражение в более читаемом формате.
Видео:Как оформить график в MatLab.Скачать

Вычислить площадь под графиком матлаб
Filled area 2-D plot
Видео:Построение освещенной поверхности. Высокоуровневая графика. Урок 37Скачать

Syntax
Видео:Математика Без Ху!ни. Полярные координаты. Построение графика функции.Скачать

Description
area( X , Y ) plots the values in Y against the x-coordinates X . The function then fills the areas between the curves based on the shape of Y :
If Y is a vector, the plot contains one curve. area fills the area between the curve and the horizontal axis.
If Y is a matrix, the plot contains one curve for each column in Y . area fills the areas between the curves and stacks them, showing the relative contribution of each row element to the total height at each x-coordinate.
area( Y ) plots Y against an implicit set of x-coordinates and fills the areas between the curves.
If Y is a vector, the x-coordinates range from 1 to length(Y) .
If Y is a matrix, the x-coordinates range from 1 to the number of rows in Y .
area( ___ , basevalue ) specifies the baseline value for the area plot. basevalue corresponds to a horizontal baseline. area fills the area confined between the curves and this line. Specify basevalue as the last argument in any of the previous syntaxes.
area( ___ , Name,Value ) modifies the properties of the area plot using one or more name-value pair arguments. The properties apply to all of the displayed areas. For example, ‘LineStyle’,’—‘ specifies a dashed line style for the plot. Specify the name-value pairs after all of the arguments in any of the previous syntaxes. For a list of properties, see Area Properties .
area( ax , ___ ) displays the area plot in the target axes. Specify the axes as the first argument in any of the previous syntaxes.
a = area( ___ ) returns one or more Area objects. The number of objects is equal to the number of plotted areas. Use a to modify properties of the areas after creating them. For a list of properties, see Area Properties .
Видео:Высокоуровневая графика. Построение графиков из окна Workspace. Урок 24Скачать

Examples
Create Area Plot with One Curve
Create a vector of four values. Display the values in an area plot.
Create Area Plot with Multiple Curves
Create matrix Y . Then display the values in Y as an area plot. Because Y contains three columns, area plots three curves and stacks them.
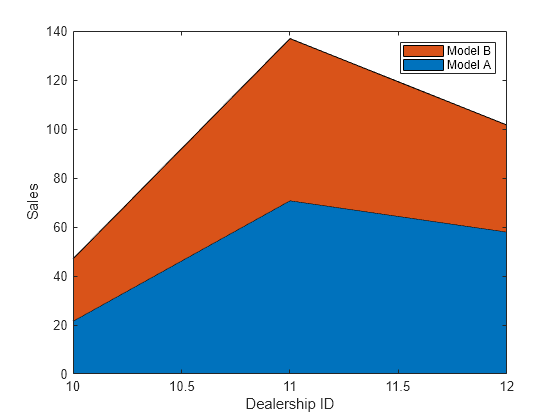
Create Area Plot Using Horizontal Axis Values
Define x as a vector of three car dealership IDs. Define Y as a matrix containing the number of cars sold per model. Display the values in the matrix in an area plot. Then add the axis labels and a legend.
Set the tick marks along the x -axis to correspond to the values in x .
Adjust Baseline Value of Area Plot
Create matrix Y . Then display the values of Y in an area plot with a baseline value of -4 . area fills the areas specified by the curves and the line y = -4 .
Specify Line Style of Area Plot
Create matrix Y . Display the values of Y in an area plot that uses a dotted line style.
Plot Filled Area into Target Axes
Create a tiled chart layout in the ‘flow’ tile arrangement, so that the axes fill the available space in the layout. Next, call the nexttile function to create an Axes object and return it as ax1 . Display an area plot by passing ax1 to the area function.
Repeat the process to create a second Axes object and a second area plot.
Change Area Characteristics After Plotting
Create matrix Y . Then create an area plot, specifying an output argument when calling the area function. In this case, area returns a vector of three Area objects. Each object corresponds to a different column of Y .
Modify the second area to be green with thick red edges.
Set Colors in Area Plot
Display an area plot with three curves.
Set the color order to blue, purple, and gray.
Видео:MatLab. Урок 3. Функции и построение графиков.Скачать

Input Arguments
X — x-coordinates
vector | matrix
x-coordinates, specified as a vector or matrix. The size and shape of X depend on the shape of your data and the type of plot you want to create. This table describes the most common situations.
| Type of Plot | How to Specify Coordinates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single area | ||||
| Stacked areas |
| Type of Plot | How to Specify Coordinates |
|---|---|
| Single area | |
| Stacked areas |