- Matlab, как рассчитать AUC (площадь под кривой)?
- 6 ответов
- Площадь под графиком матлаб
- Syntax
- Description
- Examples
- Create Area Plot with One Curve
- Create Area Plot with Multiple Curves
- Create Area Plot Using Horizontal Axis Values
- Adjust Baseline Value of Area Plot
- Specify Line Style of Area Plot
- Plot Filled Area into Target Axes
- Change Area Characteristics After Plotting
- Set Colors in Area Plot
- Input Arguments
- X — x-coordinates vector | matrix
- Y — y-coordinates vector | matrix
- basevalue — Baseline value 0 (default) | numeric scalar
- ax — Target axes Axes object
- Name-Value Arguments
- FaceColor — Area fill color RGB triplet | hexadecimal color code | ‘r’ | ‘g’ | ‘b’ | ‘flat’ | .
- MATLAB — Интеграция
- Поиск неопределенного интеграла с помощью MATLAB
- Пример 1
- Пример 2
- 📽️ Видео
Видео:MatLab. Урок 3. Функции и построение графиков.Скачать

Matlab, как рассчитать AUC (площадь под кривой)?
у меня есть файл data.txt С двумя столбцами и N строками, что-то вроде этого:
каждая пара значений в файле соответствует одной точке координат (x,y). При построении графика эти точки образуют кривую. Я хотел бы рассчитать площадь под кривой (AUC) этой кривой.
поэтому я загружаю данные:
и X содержит все X-координаты точек, а Y все координаты y.
как я мог вычислить площадь под кривой (AUC) ?
Видео:MATLAB 07 Интерактивное построение графиковСкачать

6 ответов
самый простой способ-трапециевидная функция правила trapz .
Если ваши данные, как известно, гладкие, вы можете попробовать использовать правило Симпсона, но нет ничего встроенного в MATLAB для интеграции числовых данных через правило Симпсона. (&Я не уверен, как использовать его для данных x/y, где x не увеличивается стабильно)
просто добавить AUC = trapz(X, Y) к вашей программе и вы получите площадь под кривой
Видео:Построение графиков: нахождение площади под кривойСкачать
Площадь под графиком матлаб
Filled area 2-D plot
Видео:MATLAB 08 Расширенное построение графиков: особенности и приемыСкачать

Syntax
Видео:MatLab. Создание 3D графиков. Практика 4Скачать
Description
area( X , Y ) plots the values in Y against the x-coordinates X . The function then fills the areas between the curves based on the shape of Y :
If Y is a vector, the plot contains one curve. area fills the area between the curve and the horizontal axis.
If Y is a matrix, the plot contains one curve for each column in Y . area fills the areas between the curves and stacks them, showing the relative contribution of each row element to the total height at each x-coordinate.
area( Y ) plots Y against an implicit set of x-coordinates and fills the areas between the curves.
If Y is a vector, the x-coordinates range from 1 to length(Y) .
If Y is a matrix, the x-coordinates range from 1 to the number of rows in Y .
area( ___ , basevalue ) specifies the baseline value for the area plot. basevalue corresponds to a horizontal baseline. area fills the area confined between the curves and this line. Specify basevalue as the last argument in any of the previous syntaxes.
area( ___ , Name,Value ) modifies the properties of the area plot using one or more name-value pair arguments. The properties apply to all of the displayed areas. For example, ‘LineStyle’,’—‘ specifies a dashed line style for the plot. Specify the name-value pairs after all of the arguments in any of the previous syntaxes. For a list of properties, see Area Properties .
area( ax , ___ ) displays the area plot in the target axes. Specify the axes as the first argument in any of the previous syntaxes.
a = area( ___ ) returns one or more Area objects. The number of objects is equal to the number of plotted areas. Use a to modify properties of the areas after creating them. For a list of properties, see Area Properties .
Видео:Математика это не ИсламСкачать

Examples
Create Area Plot with One Curve
Create a vector of four values. Display the values in an area plot.
Create Area Plot with Multiple Curves
Create matrix Y . Then display the values in Y as an area plot. Because Y contains three columns, area plots three curves and stacks them.
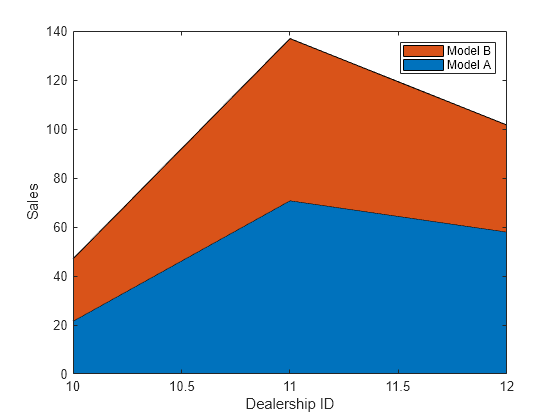
Create Area Plot Using Horizontal Axis Values
Define x as a vector of three car dealership IDs. Define Y as a matrix containing the number of cars sold per model. Display the values in the matrix in an area plot. Then add the axis labels and a legend.
Set the tick marks along the x -axis to correspond to the values in x .
Adjust Baseline Value of Area Plot
Create matrix Y . Then display the values of Y in an area plot with a baseline value of -4 . area fills the areas specified by the curves and the line y = -4 .
Specify Line Style of Area Plot
Create matrix Y . Display the values of Y in an area plot that uses a dotted line style.
Plot Filled Area into Target Axes
Create a tiled chart layout in the ‘flow’ tile arrangement, so that the axes fill the available space in the layout. Next, call the nexttile function to create an Axes object and return it as ax1 . Display an area plot by passing ax1 to the area function.
Repeat the process to create a second Axes object and a second area plot.
Change Area Characteristics After Plotting
Create matrix Y . Then create an area plot, specifying an output argument when calling the area function. In this case, area returns a vector of three Area objects. Each object corresponds to a different column of Y .
Modify the second area to be green with thick red edges.
Set Colors in Area Plot
Display an area plot with three curves.
Set the color order to blue, purple, and gray.
Видео:Как оформить график в MatLab.Скачать

Input Arguments
X — x-coordinates
vector | matrix
x-coordinates, specified as a vector or matrix. The size and shape of X depend on the shape of your data and the type of plot you want to create. This table describes the most common situations.
| Type of Plot | How to Specify Coordinates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single area | ||||
| Stacked areas |
| Type of Plot | How to Specify Coordinates |
|---|---|
| Single area | |
| Stacked areas |